Ramachandran Plot and N-terminal Protein Sequencing Method
Part A: Ramachandran Plot
Definition:
A Ramachandran plot is a graphical representation that shows the possible combinations of dihedral angles (phi φ and psi ψ) of amino acids in a protein structure. It helps visualize allowed and disallowed conformations due to steric hindrance.
Diagram:
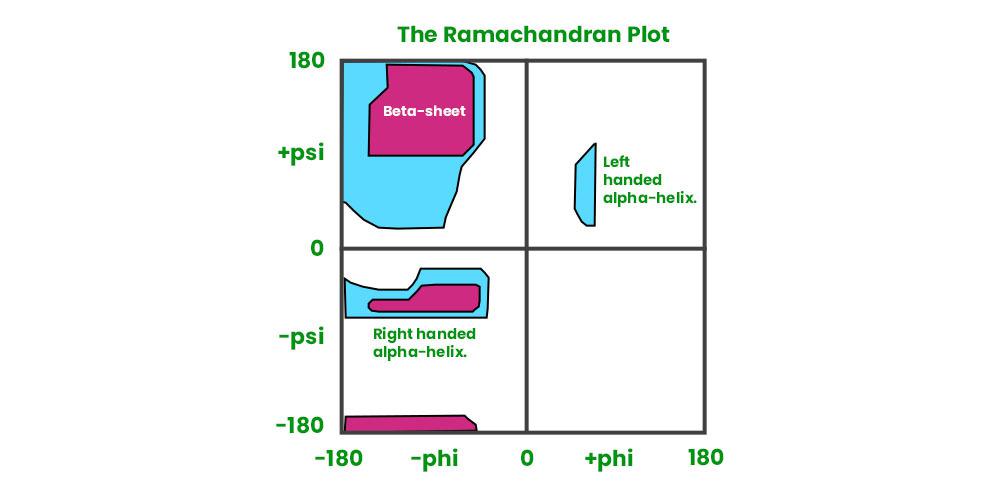
Importance:
- Helps in validating protein 3D structures obtained from X-ray crystallography or NMR.
- Identifies regions with favorable backbone conformations.
- Used to assess the quality of protein models in structural biology.
Allowed Regions:
- Alpha helix: φ ≈ -60°, ψ ≈ -40°
- Beta sheet: φ ≈ -120°, ψ ≈ 120°
- Left-handed helix: φ ≈ 60°, ψ ≈ 60°
Part B: N-terminal Protein Sequencing Method
Definition:
The N-terminal sequencing method identifies the sequence of amino acids starting from the amino (N) end of a protein. The most common method used is Edman degradation.
Steps in Edman Degradation:
- Labeling: The N-terminal amino acid reacts with phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) under alkaline conditions to form a phenylthiocarbamoyl (PTC) derivative.
- Cleavage: The PTC-amino acid is selectively cleaved without breaking other peptide bonds.
- Identification: The cleaved amino acid is converted into a stable phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) derivative and identified using chromatography or electrophoresis.
- Repeat: The cycle repeats for 20–30 residues to determine the N-terminal sequence.
Advantages:
- Provides direct information about the amino acid sequence
- Useful for identifying unknown proteins
Limitations:
- Cannot sequence beyond 30–50 residues efficiently
- Blocked N-termini (e.g., acetylated) must be modified before sequencing
Conclusion
Both the Ramachandran plot and N-terminal sequencing are fundamental tools in protein biochemistry. The plot is essential for understanding protein folding and structural validation, while N-terminal sequencing helps determine the identity and structure of proteins. Together, they enhance our understanding of protein structure and function.